P&ID Tutorial
Usually dispatched in 2 to 3 days
Usually dispatched in 2 to 3 days
Category:
Hydraulic , Piping & Fittings
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Related products
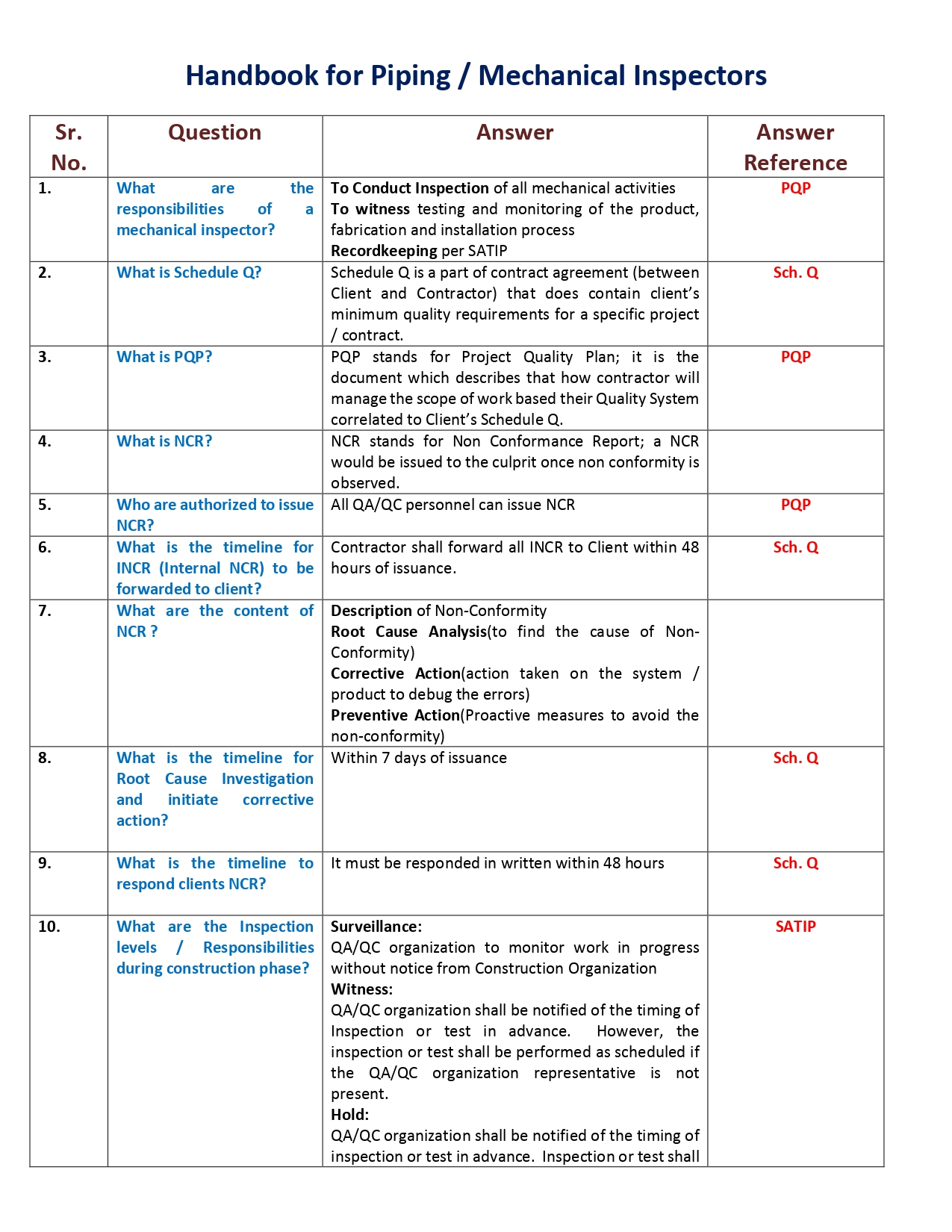
Inspect New Piping
Piping systems are like arteries and veins in the oil industry. Piping systems comprise of pipes, flanges, bolting, gaskets, valves etc. They also include pipe hangers, supporting elements and other items necessary to prevent over pressurization and over stressing of the pressure containing components. Hence, one can say that pipe section when fitted with valves and other mechanical equipment and properly supported by hangers and supports are called piping.
Inspect New Piping
Piping systems are like arteries and veins in the oil industry. Piping systems comprise of pipes, flanges, bolting, gaskets, valves etc. They also include pipe hangers, supporting elements and other items necessary to prevent over pressurization and over stressing of the pressure containing components. Hence, one can say that pipe section when fitted with valves and other mechanical equipment and properly supported by hangers and supports are called piping.
Considerations in the Hydraulic Design of Pipelines
The report summarises the findings of pipe reviews which were conducted during the research project
and highlights the following actions which should be considered during the hydraulic design of
pipelines :
• Review and incorporate available recorded hydraulic performance data of pipelines in the region in the design of new infrastructure;
• Include the secondary energy loss associated with the dimensional details of the couplings in the calculation of the energy loss in the pipeline;
• Use the proposed BRM (biofilm resistance model) to calculate a representative roughness for biofouled pipelines;
• Implement the proposed procedure to determine the remaining useful life of pipelines to be able to prioritize the upgrading or replacement of system components; and
• Provide monitoring points for the initial, continuous or intermittent hydraulic assessment of the pipeline.
Considerations in the Hydraulic Design of Pipelines
The report summarises the findings of pipe reviews which were conducted during the research project
and highlights the following actions which should be considered during the hydraulic design of
pipelines :
• Review and incorporate available recorded hydraulic performance data of pipelines in the region in the design of new infrastructure;
• Include the secondary energy loss associated with the dimensional details of the couplings in the calculation of the energy loss in the pipeline;
• Use the proposed BRM (biofilm resistance model) to calculate a representative roughness for biofouled pipelines;
• Implement the proposed procedure to determine the remaining useful life of pipelines to be able to prioritize the upgrading or replacement of system components; and
• Provide monitoring points for the initial, continuous or intermittent hydraulic assessment of the pipeline.
Presentation on Fundamentals of Pipeline Design
➢The amount of fluid flow through the pipeline is one of the first items of information required for design
➢ Different industries use pipeline for different purposes. requirements & types of pipe are different
➢ Petroleum industry & natural gas industry use steel pipe with welded joints.
➢ This allows the pipeline to withstand very high pressure, sometimes above 3000 psig
➢ High pressure allow the use of long pipelines, often more then 1000 miles with only a booster pump or station for each pipeline
➢ Some pipelines are designed with some excess capacity or design so capacity can be increased by the addition of compression or pumping horsepower
Presentation on Fundamentals of Pipeline Design
➢The amount of fluid flow through the pipeline is one of the first items of information required for design
➢ Different industries use pipeline for different purposes. requirements & types of pipe are different
➢ Petroleum industry & natural gas industry use steel pipe with welded joints.
➢ This allows the pipeline to withstand very high pressure, sometimes above 3000 psig
➢ High pressure allow the use of long pipelines, often more then 1000 miles with only a booster pump or station for each pipeline
➢ Some pipelines are designed with some excess capacity or design so capacity can be increased by the addition of compression or pumping horsepower













Reviews
There are no reviews yet.