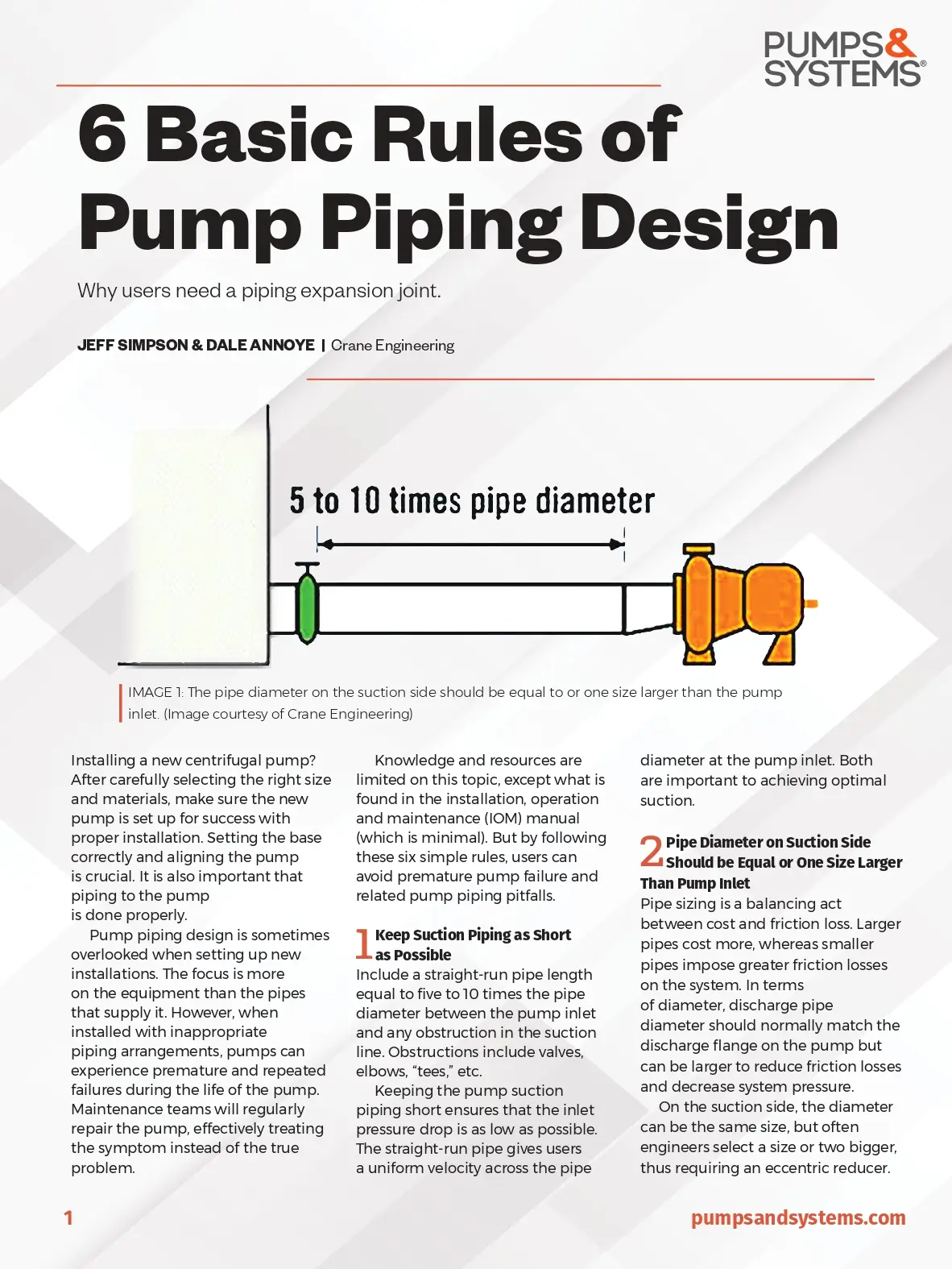
6 Basic Rules Of Pump Piping Design
6 Basic Rules Of Pump Piping Design
Source: https://www.pumpsandsystems.com
Prepared By: Jeff Simpson & Dale Annoye
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Related books
Chapter10. Compressors
Chapter10. Compressors
Guide To The Selection Of Rotodynamic Pumps
Guide To The Selection Of Rotodynamic Pumps
Optimum Operation Management Effect of Main Sewage Pumping Stations on Trunk Sewer Deterioration
Sewage pumping stations are considered an important part of any sewerage system. Pumps failure in these stations means that the pumps are unable to work at the design requirement (flow capacity and head) and that may cause sewer overflow and flooding leading to sewer deterioration. In this paper, two main sewage pumping stations in Baghdad city were selected as case studies, Al[1]Habibia and Al-Ghazali located on Zublin trunk sewer 3000 mm and Baghdad trunk sewer 1200-2100 respectively. This study focused mainly on the operation of main sewage pumping stations and their effect, both directly and indirectly, on changing hydraulic properties, which leads to an increase in the deterioration of sewage pipes. The hydraulic analysis was conducted to investigate the effect of the operational performance of these stations on the deterioration of the trunk sewers. In general, the sewage pumps are in good condition based on the completed evaluation of these stations but, it was observed that Al-Habibia sewage pumping station was unable to discharge high sewage flow (d/D = 0.75). Backup flow occurred in the inlet sewer and caused overflow and flooding. The hydraulic analysis for the effluent sewer showed that the actual flowing velocities of the operating conditions examined were greater than the minimum self[1]cleaning velocity. Al-Ghazali sewage pumping station was able to receive the influent sewage for all the cases of flow (low, medium and high). While the effluent sewer (Baghdad trunk sewer) that was 70% filled with sediments, that reduced its capacity, does not work with the high discharges of the pumps. Therefore, resulting in sewage flows from this overloaded sewer onto the streets and harms the environment. Keywords: Hydraulic analysis, Operational performance evaluation, Pumps condition, Sewage pumping stations, Trunk sewer deterioration.
Optimum Operation Management Effect of Main Sewage Pumping Stations on Trunk Sewer Deterioration
Sewage pumping stations are considered an important part of any sewerage system. Pumps failure in these stations means that the pumps are unable to work at the design requirement (flow capacity and head) and that may cause sewer overflow and flooding leading to sewer deterioration. In this paper, two main sewage pumping stations in Baghdad city were selected as case studies, Al[1]Habibia and Al-Ghazali located on Zublin trunk sewer 3000 mm and Baghdad trunk sewer 1200-2100 respectively. This study focused mainly on the operation of main sewage pumping stations and their effect, both directly and indirectly, on changing hydraulic properties, which leads to an increase in the deterioration of sewage pipes. The hydraulic analysis was conducted to investigate the effect of the operational performance of these stations on the deterioration of the trunk sewers. In general, the sewage pumps are in good condition based on the completed evaluation of these stations but, it was observed that Al-Habibia sewage pumping station was unable to discharge high sewage flow (d/D = 0.75). Backup flow occurred in the inlet sewer and caused overflow and flooding. The hydraulic analysis for the effluent sewer showed that the actual flowing velocities of the operating conditions examined were greater than the minimum self[1]cleaning velocity. Al-Ghazali sewage pumping station was able to receive the influent sewage for all the cases of flow (low, medium and high). While the effluent sewer (Baghdad trunk sewer) that was 70% filled with sediments, that reduced its capacity, does not work with the high discharges of the pumps. Therefore, resulting in sewage flows from this overloaded sewer onto the streets and harms the environment. Keywords: Hydraulic analysis, Operational performance evaluation, Pumps condition, Sewage pumping stations, Trunk sewer deterioration.










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.