Pumps & Mechanical
Analytical Analysis And Maintenance Of A Centrifugal Pump
Views : 6
Analytical Analysis And Maintenance Of A Centrifugal Pump
Source: https://www.univ-ouargla.dz/
Prepared By: Ilyas Krizou, Aissa Bouabboune
Usually dispatched in 2 to 3 days
Usually dispatched in 2 to 3 days
Category:
Pumps & Mechanical
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Related books
Fire Pump Systems Design and Specification
Think your fire pumps are just like the rest of your fluid movers? Think again. Rigorous standards and certifications make sure these life-savers are up to snuff
Fire Pump Systems Design and Specification
Think your fire pumps are just like the rest of your fluid movers? Think again. Rigorous standards and certifications make sure these life-savers are up to snuff
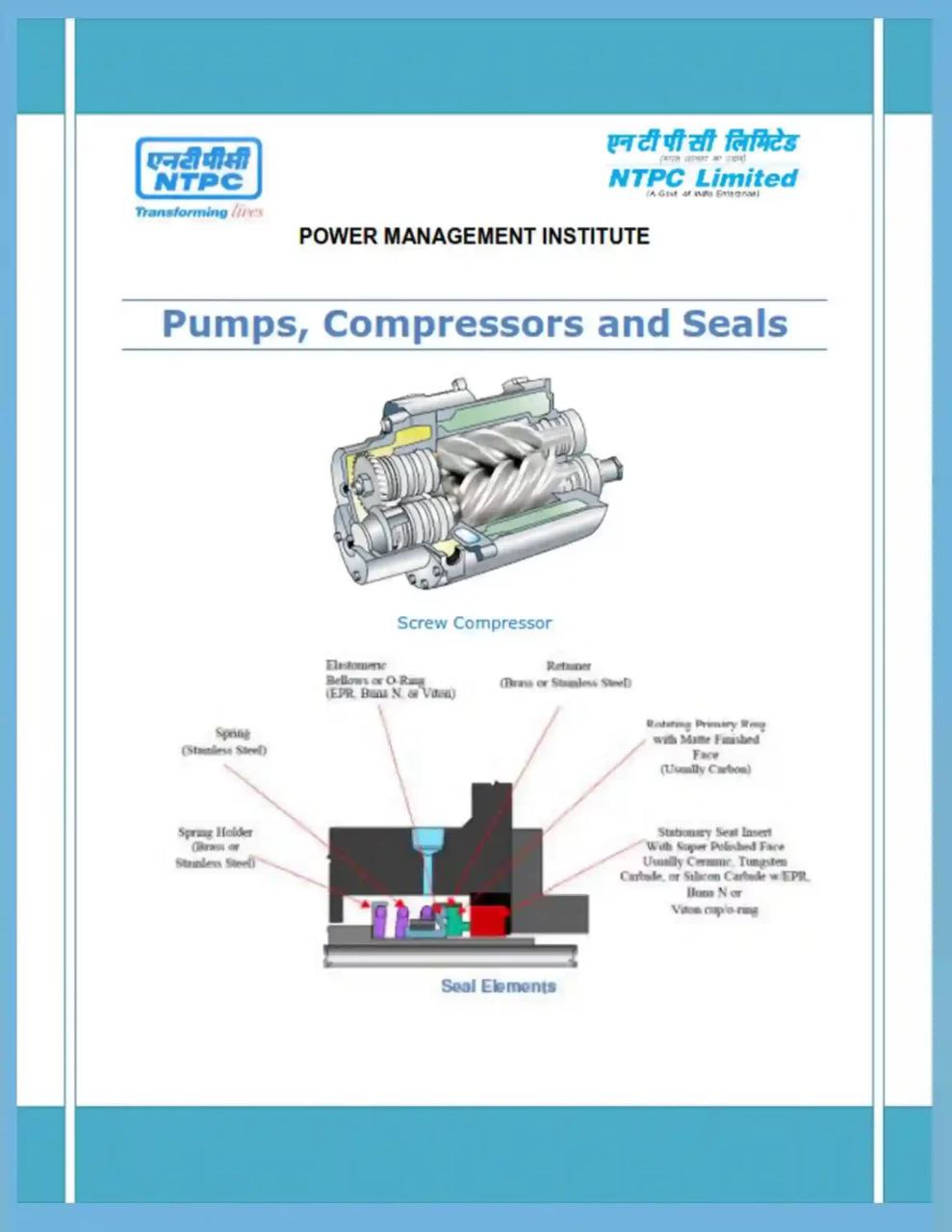
Pumps, Compressors and Seals
The most numerous types of fluid machineries are of the pump family (machines which add energy to the fluid), other important types are turbines (which extract energy from fluid). Both types are usually connected to a rotating shaft, hence also called turbomachineries. The prefix turbo- is a Latin word meaning ―spin’’ or ―whirl,’’ appropriate for rotating devices. The pump is the oldest fluid-energy-transfer device known. At least two designs date before Christ: (i) the undershot-bucket waterwheels, or norias, used in Asia and Africa (1000 B.C.) and (ii) Archimedes’ screw pump (250 B.C.), still being manufactured today to handle solid-liquid mixtures or to raise water from the hold of a ship. Paddlewheel turbines were used by the Romans in 70 B.C., and Babylonian windmills date back to 700 B.C. Since that time, many variations and applications of pumps have been developed. The power generating turbomachines (turbines) decrease the head or energy level of the working fluids passing through them and they are coupled to machines, such as electric generators, pumps, compressors etc.
Pumps, Compressors and Seals
The most numerous types of fluid machineries are of the pump family (machines which add energy to the fluid), other important types are turbines (which extract energy from fluid). Both types are usually connected to a rotating shaft, hence also called turbomachineries. The prefix turbo- is a Latin word meaning ―spin’’ or ―whirl,’’ appropriate for rotating devices. The pump is the oldest fluid-energy-transfer device known. At least two designs date before Christ: (i) the undershot-bucket waterwheels, or norias, used in Asia and Africa (1000 B.C.) and (ii) Archimedes’ screw pump (250 B.C.), still being manufactured today to handle solid-liquid mixtures or to raise water from the hold of a ship. Paddlewheel turbines were used by the Romans in 70 B.C., and Babylonian windmills date back to 700 B.C. Since that time, many variations and applications of pumps have been developed. The power generating turbomachines (turbines) decrease the head or energy level of the working fluids passing through them and they are coupled to machines, such as electric generators, pumps, compressors etc.
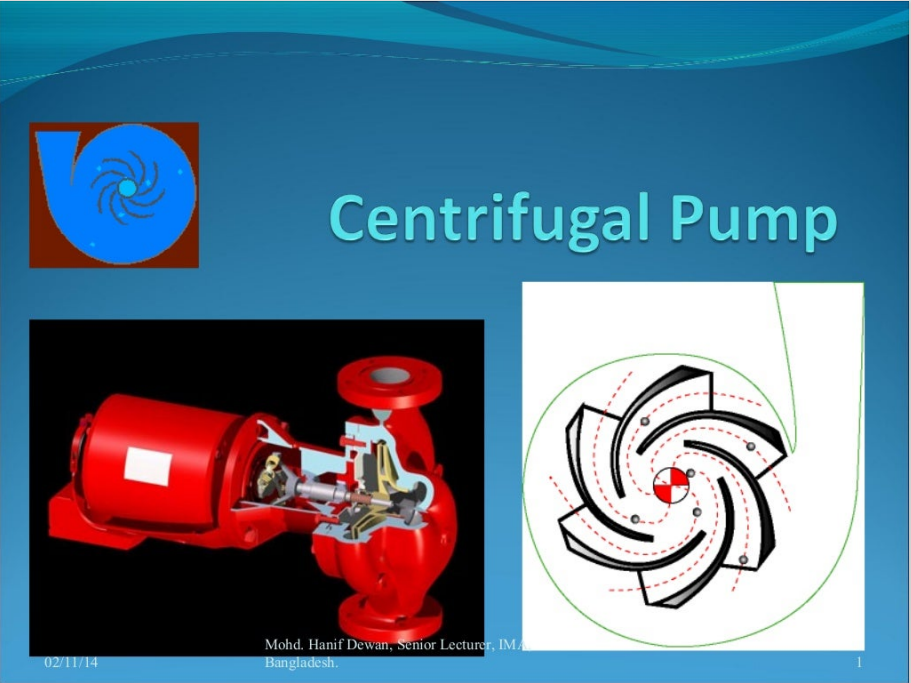
Centrifugal Pump Analysis
Introduction
Centrifugal pumps are used to increase pressure in a liquid for the purpose of transporting the liquid through piping and other devices for use in an industrial process. With the higher pressure, the liquid can be transported in short or long pipelines for delivery to an ultimate destination. Examples include water pipelines, refined petroleum and crude oil pipelines.
The pressure generated by the pump is gradually depleted as the liquid flows through the pipeline, due to friction in the pipe, as well as any elevation increase from the point of origin to the destination point. The liquid as it enters the pump has a certain amount of energy, due to its initial pressure (pressure energy), position (potential energy) and its velocity (kinetic energy). The potential energy depends on the location of the liquid from some datum, such as sea level. The kinetic energy is due to the motion of the liquid. The sum of three components is the total energy of the liquid. As the liquid comes out of the pump, energy is imparted by the rotating element (impeller) in the pump and the liquid pressure increases. The velocity of the liquid also changes from that at the pump inlet. In a centrifugal pump, the liquid is accelerated by centrifugal force during its passage through the rotating pump impeller and, finally at the exit, the kinetic energy is converted to pressure energy as it exits the pump volute into the discharge piping.
Centrifugal Pump Analysis
Introduction
Centrifugal pumps are used to increase pressure in a liquid for the purpose of transporting the liquid through piping and other devices for use in an industrial process. With the higher pressure, the liquid can be transported in short or long pipelines for delivery to an ultimate destination. Examples include water pipelines, refined petroleum and crude oil pipelines.
The pressure generated by the pump is gradually depleted as the liquid flows through the pipeline, due to friction in the pipe, as well as any elevation increase from the point of origin to the destination point. The liquid as it enters the pump has a certain amount of energy, due to its initial pressure (pressure energy), position (potential energy) and its velocity (kinetic energy). The potential energy depends on the location of the liquid from some datum, such as sea level. The kinetic energy is due to the motion of the liquid. The sum of three components is the total energy of the liquid. As the liquid comes out of the pump, energy is imparted by the rotating element (impeller) in the pump and the liquid pressure increases. The velocity of the liquid also changes from that at the pump inlet. In a centrifugal pump, the liquid is accelerated by centrifugal force during its passage through the rotating pump impeller and, finally at the exit, the kinetic energy is converted to pressure energy as it exits the pump volute into the discharge piping.
Chapter One Introduction To Reciprocating Compressors
Introduction
Compressors are used whenever it is necessary to flow gas from a low-pressure system to a higher-pressure system. Flash gas from low-pressure vessels used for multi-stage stabilization of liquids, oil treating, water treating, etc.; often exists at too low a pressure to flow into the gas sales pipeline. Sometimes this gas is used as fuel, and them the remainder is flared or vented. In many instances, it is economically attractive to compress this gas to a high enough pressure so it can be sold. Compression may also be required for environmental reasons. Flash gas that might otherwise be flared may be compressed for sales or gas produced with oil (associated gas) may be compressed for re-injection to avoid, flaring or to help maintain reservoir pressure. In some marginal gas fields, and in many larger gas fields that experience a decline in flowing pressure with time, it may be economical to allow the wells to flow at surface pressures below that required for gas sales. In such cases, a booster compressor (one where the ratio of discharge to suction pressure is low) may be installed. Booster compressors are also used on long pipelines to restore pressure drop lost to friction. The use of large compressors is probably more prevalent in oil field facilities than in gas field facilities. Oil wells often require low flowing surface pressures and the gas that flashes off the oil in the separator must be compressed. Often, natural gas is, injected into the tubing of the well to lighten the column of liquid and reduce downhole pressure. This "gas lift" gas is produced back with good fluids at low pressure. Compressors are used so the lift gas can be recirculated and
Chapter One Introduction To Reciprocating Compressors
Introduction
Compressors are used whenever it is necessary to flow gas from a low-pressure system to a higher-pressure system. Flash gas from low-pressure vessels used for multi-stage stabilization of liquids, oil treating, water treating, etc.; often exists at too low a pressure to flow into the gas sales pipeline. Sometimes this gas is used as fuel, and them the remainder is flared or vented. In many instances, it is economically attractive to compress this gas to a high enough pressure so it can be sold. Compression may also be required for environmental reasons. Flash gas that might otherwise be flared may be compressed for sales or gas produced with oil (associated gas) may be compressed for re-injection to avoid, flaring or to help maintain reservoir pressure. In some marginal gas fields, and in many larger gas fields that experience a decline in flowing pressure with time, it may be economical to allow the wells to flow at surface pressures below that required for gas sales. In such cases, a booster compressor (one where the ratio of discharge to suction pressure is low) may be installed. Booster compressors are also used on long pipelines to restore pressure drop lost to friction. The use of large compressors is probably more prevalent in oil field facilities than in gas field facilities. Oil wells often require low flowing surface pressures and the gas that flashes off the oil in the separator must be compressed. Often, natural gas is, injected into the tubing of the well to lighten the column of liquid and reduce downhole pressure. This "gas lift" gas is produced back with good fluids at low pressure. Compressors are used so the lift gas can be recirculated and
Pumps In Water Treatment
INTRODUCTION : 1.1 Why water treatment?
Pure water [H2O] is a colourless, odourless and tasteless liquid. It plays a huge part in everyday life: 70% of the earth’s surface is covered by water in the form of oceans, and the rest of the planet has large quantities of water in the form of lakes, rivers and watercourses, ice and snow, and humidity, as well as the principal element of animal life (>50%) and plants (approx. 80%). When we talk about water in general, we usually mean water for some specific purpose, e.g. drinking water or process water for industry. This is where the term water treatment comes into the picture, as the available water resources or that provided by nature is not always of a suitable quality for immediate use for the specific purpose. Drinking water must be pure, and should preferably taste good too, and it must not contain substances that could cause problemswith daily use. Process water, which is water that forms a direct and important part of a process or product in industry, must have a chemical composition and temperature that is precisely suited to the specific requirements.
Pumps In Water Treatment
INTRODUCTION : 1.1 Why water treatment?
Pure water [H2O] is a colourless, odourless and tasteless liquid. It plays a huge part in everyday life: 70% of the earth’s surface is covered by water in the form of oceans, and the rest of the planet has large quantities of water in the form of lakes, rivers and watercourses, ice and snow, and humidity, as well as the principal element of animal life (>50%) and plants (approx. 80%). When we talk about water in general, we usually mean water for some specific purpose, e.g. drinking water or process water for industry. This is where the term water treatment comes into the picture, as the available water resources or that provided by nature is not always of a suitable quality for immediate use for the specific purpose. Drinking water must be pure, and should preferably taste good too, and it must not contain substances that could cause problemswith daily use. Process water, which is water that forms a direct and important part of a process or product in industry, must have a chemical composition and temperature that is precisely suited to the specific requirements.
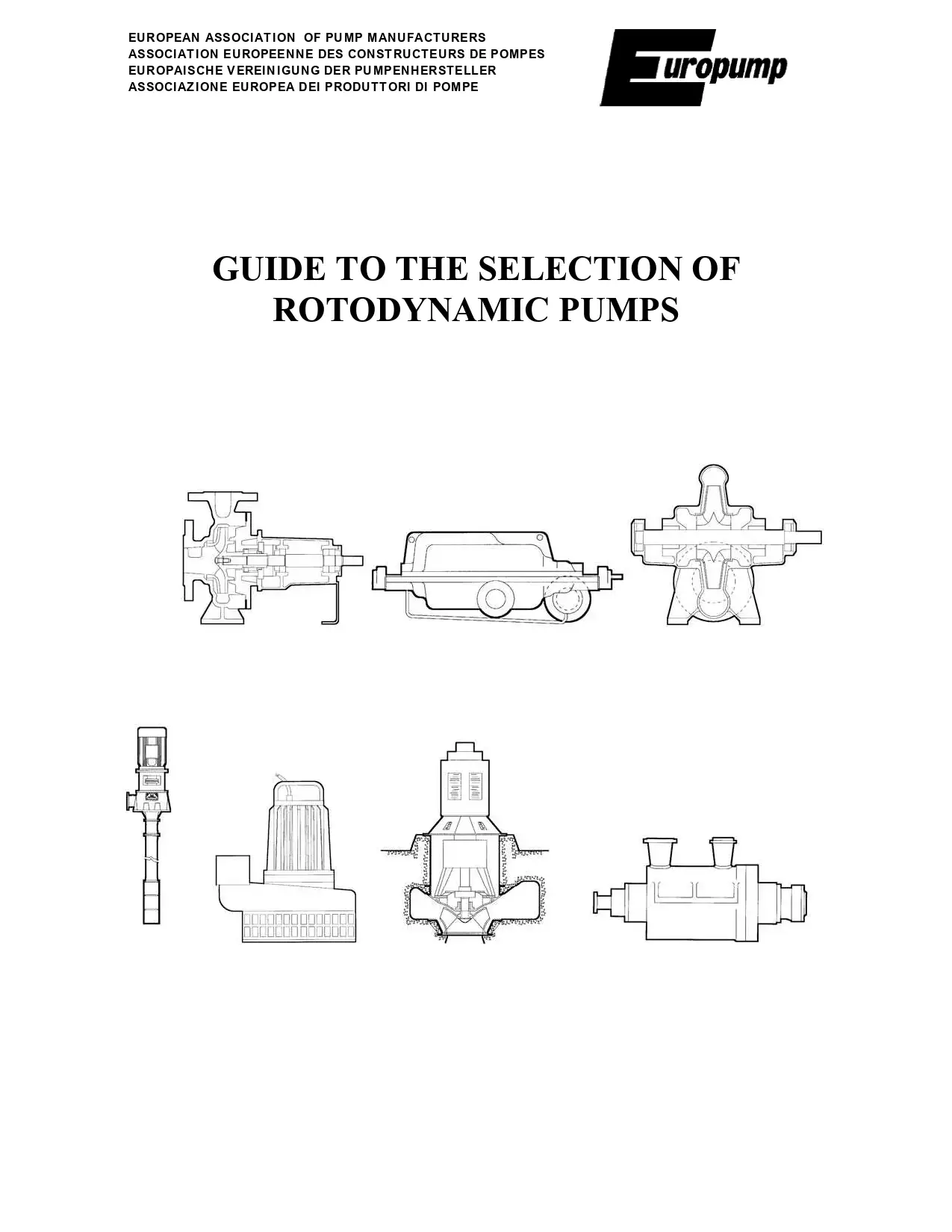
Guide To The Selection Of Rotodynamic Pumps
Purpose of this Guide to pump procurement
This Guide provides an introduction to the very complex subject of the selection of pumps. It is aimed at anyone who wishes to purchase or select a pump and, at the same time, wishes to save money on their energy bill. Almost invariably, this saving will be far more than the first cost of the pump. The reader may be the end user, a contractor, or a consultant. This Guide provides the reader with the basic principles of pump procurement, giving pointers to the pump type and performance they should consider. Pumps are divided into their main types, then their basic construction and performance are considered, their principal applications are described, the basic principles of pump selection are explained and, last but not least, target efficiencies are set to help minimize energy usage. The hope is that both pump users and the environment will benefit.
Guide To The Selection Of Rotodynamic Pumps
Purpose of this Guide to pump procurement
This Guide provides an introduction to the very complex subject of the selection of pumps. It is aimed at anyone who wishes to purchase or select a pump and, at the same time, wishes to save money on their energy bill. Almost invariably, this saving will be far more than the first cost of the pump. The reader may be the end user, a contractor, or a consultant. This Guide provides the reader with the basic principles of pump procurement, giving pointers to the pump type and performance they should consider. Pumps are divided into their main types, then their basic construction and performance are considered, their principal applications are described, the basic principles of pump selection are explained and, last but not least, target efficiencies are set to help minimize energy usage. The hope is that both pump users and the environment will benefit.










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.