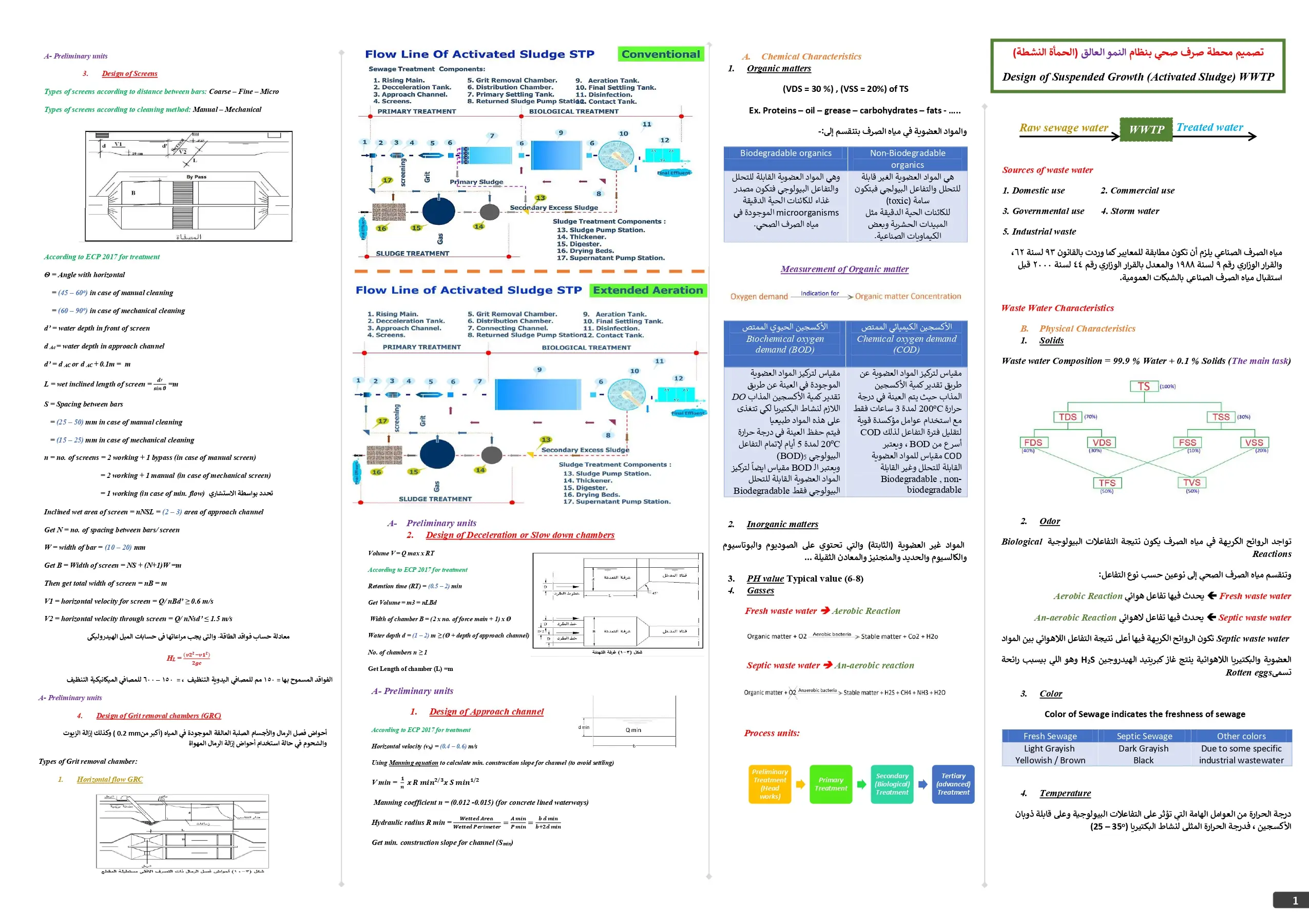
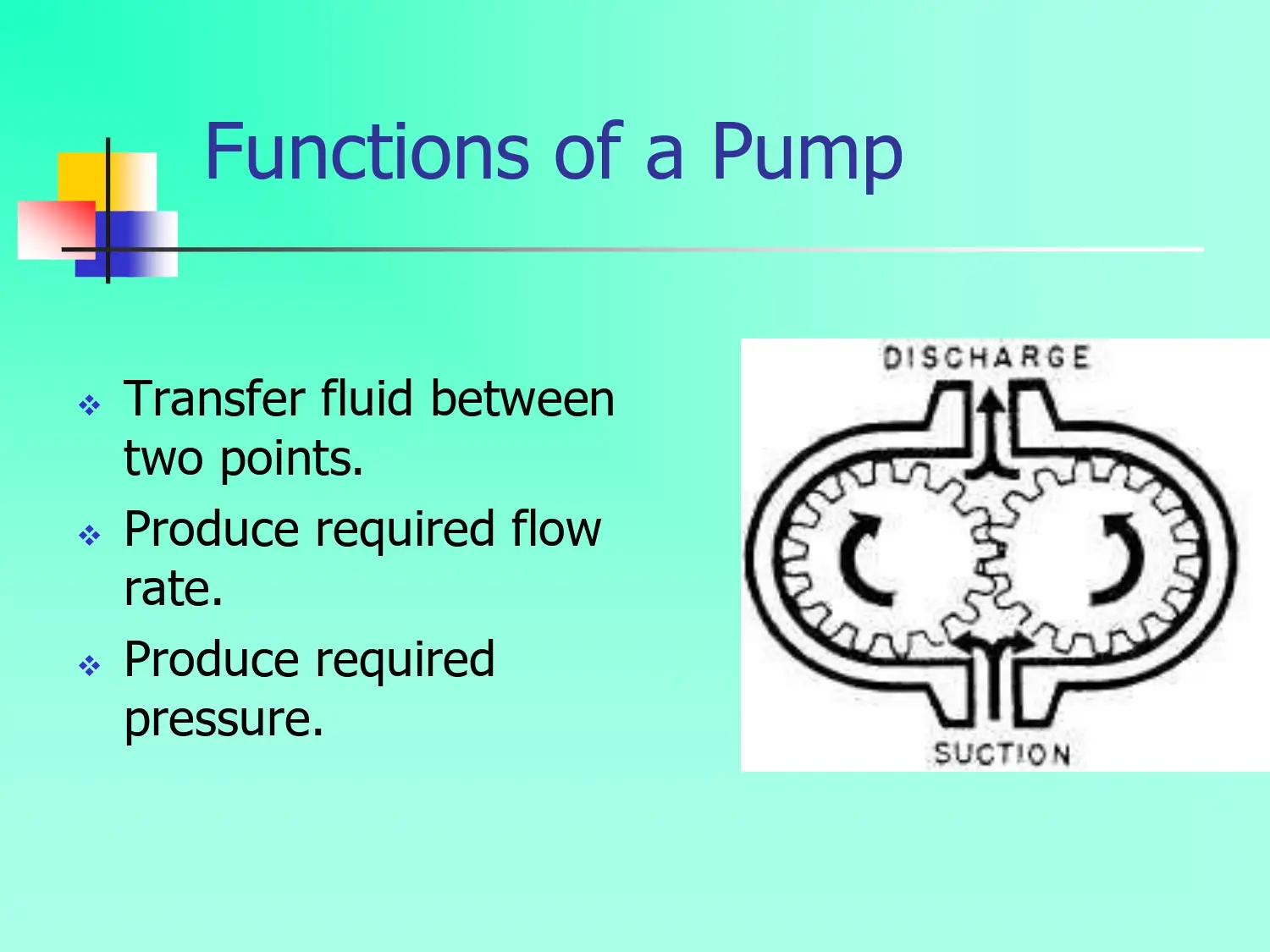
The Next Steps for Sustainable Business
Twenty-twenty-four may very well become a breakthrough year for sustainability. Although, as always, the world’s sustainability transformation will labor forward amidst many other pressing concerns, this year inherited considerable momentum from 2023, including the historic outcomes of COP28 and the decisive global embrace of simultaneous action on climate, nature, and equity.
The Next Steps for Sustainable Business
Twenty-twenty-four may very well become a breakthrough year for sustainability. Although, as always, the world’s sustainability transformation will labor forward amidst many other pressing concerns, this year inherited considerable momentum from 2023, including the historic outcomes of COP28 and the decisive global embrace of simultaneous action on climate, nature, and equity.
The Circularity Gap Report 2024
Despite the circular economy entering the mainstream, global circularity is still in decline. Over the past five years, the volume of discussions, debates, and articles addressing this topic has almost tripled, reflecting a heightened awareness and interest in circularity. However, the vast majority of extracted materials entering the economy are virgin, with the share of secondary materials declining steadily since the Circularity Gap Report began measuring it: from 9.1% in 2018 to 7.2% just five years later in 2023.1 Meanwhile, the total amount of materials consumed by the global economy continues to rise: in just the past six years alone we have consumed over half a trillion tonnes of materials—nearly as much as the entirety of the 20th century. These statistics display the cold, hard truth: despite the circular economy reaching ‘megatrend’ status, lofty speeches and targets are not yet translating into on-the-ground actions and
measurable impacts. Without bold, urgent action to shift to a circular economy, we'll miss out on achieving broader social and environmental goals—ranging from emissions reductions to boosting the use of secondary materials—putting industries and governments at risk of sleepwalking into circular washing and missing out on much-needed impact.
The Circularity Gap Report 2024
Despite the circular economy entering the mainstream, global circularity is still in decline. Over the past five years, the volume of discussions, debates, and articles addressing this topic has almost tripled, reflecting a heightened awareness and interest in circularity. However, the vast majority of extracted materials entering the economy are virgin, with the share of secondary materials declining steadily since the Circularity Gap Report began measuring it: from 9.1% in 2018 to 7.2% just five years later in 2023.1 Meanwhile, the total amount of materials consumed by the global economy continues to rise: in just the past six years alone we have consumed over half a trillion tonnes of materials—nearly as much as the entirety of the 20th century. These statistics display the cold, hard truth: despite the circular economy reaching ‘megatrend’ status, lofty speeches and targets are not yet translating into on-the-ground actions and
measurable impacts. Without bold, urgent action to shift to a circular economy, we'll miss out on achieving broader social and environmental goals—ranging from emissions reductions to boosting the use of secondary materials—putting industries and governments at risk of sleepwalking into circular washing and missing out on much-needed impact.
Tides of Change (A Framework for Developing Just and Inclusive Green Shipping Corridors)
Transitioning to zero and near-zero emission economies is at the core of addressing the three planetary crises outlined by the UN: climate change, biodiversity loss, and pollution currently underway.1 However, decarbonization cannot be treated in isolation. As
recognized in the 17 UN Sustainable Development Goals, “ending poverty and other deprivations must go hand-in-hand with strategies that improve health and education, reduce inequality, and spur economic growth – all while tackling climate change and working
to preserve our oceans and forests.”
Tides of Change (A Framework for Developing Just and Inclusive Green Shipping Corridors)
Transitioning to zero and near-zero emission economies is at the core of addressing the three planetary crises outlined by the UN: climate change, biodiversity loss, and pollution currently underway.1 However, decarbonization cannot be treated in isolation. As
recognized in the 17 UN Sustainable Development Goals, “ending poverty and other deprivations must go hand-in-hand with strategies that improve health and education, reduce inequality, and spur economic growth – all while tackling climate change and working
to preserve our oceans and forests.”
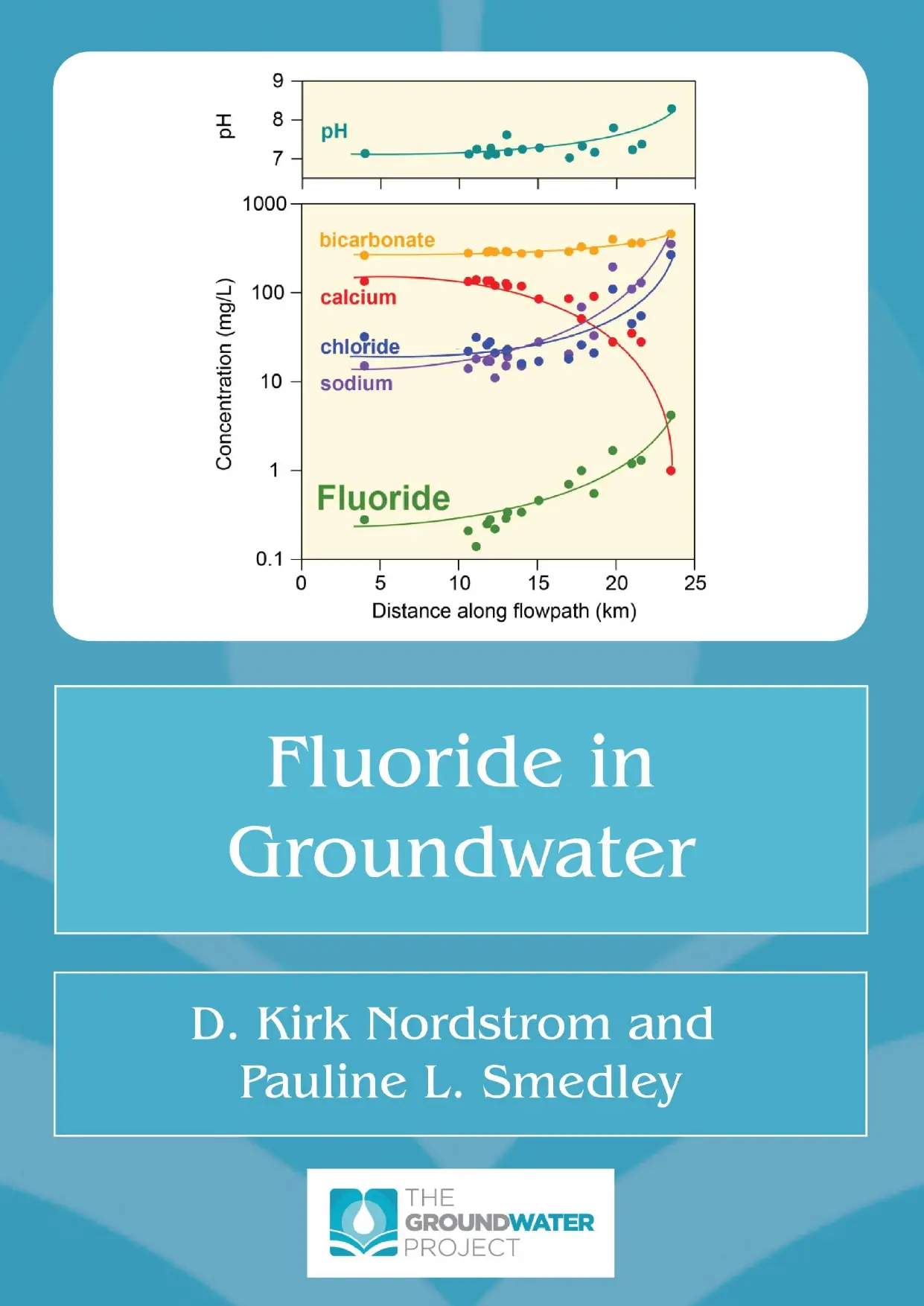
Fluoride in Groundwater
The United Nations theme for World Water Day on March 22, 2022, is “Groundwater: making the invisible visible.” This aligns with the essence of the Groundwater Project (GW-Project), which is aimed at raising groundwater consciousness and strengthening groundwater expertise worldwide, and is being accomplished by publishing books and supporting materials about “all-things-groundwater”.
Fluoride in Groundwater
The United Nations theme for World Water Day on March 22, 2022, is “Groundwater: making the invisible visible.” This aligns with the essence of the Groundwater Project (GW-Project), which is aimed at raising groundwater consciousness and strengthening groundwater expertise worldwide, and is being accomplished by publishing books and supporting materials about “all-things-groundwater”.
Hydrogen Supply for Steelmaking’s Energy Transition
In the pursuit of low-carbon technologies and sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels essential to hand on to future generations a safe and livable planet, hydrogen has attracted engineering interest as a promising vector for storing and carrying clean energy that would help decarbonize society. Scientific research and technological trends indicate that heavy industries, especially steelmaking, might represent an excellent opportunity to consistently integrate the consumption of hydrogen into the manufacturing processes. This is likely to deliver substantial emissions savings as the steel industry, widely recognized to be a hard-to-abate sector, accounts for a large portion of the global pollution every year. Besides the heated debate on the technical and financial challenges related to deployment constraints and cost increases, the geopolitical risk of energy crises impacting the economic output of industries in energy-importing countries is neglected in the decision-making considerations, overlooking the critical implications of energy diversification on long-term planning.
Hydrogen Supply for Steelmaking’s Energy Transition
In the pursuit of low-carbon technologies and sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels essential to hand on to future generations a safe and livable planet, hydrogen has attracted engineering interest as a promising vector for storing and carrying clean energy that would help decarbonize society. Scientific research and technological trends indicate that heavy industries, especially steelmaking, might represent an excellent opportunity to consistently integrate the consumption of hydrogen into the manufacturing processes. This is likely to deliver substantial emissions savings as the steel industry, widely recognized to be a hard-to-abate sector, accounts for a large portion of the global pollution every year. Besides the heated debate on the technical and financial challenges related to deployment constraints and cost increases, the geopolitical risk of energy crises impacting the economic output of industries in energy-importing countries is neglected in the decision-making considerations, overlooking the critical implications of energy diversification on long-term planning.
Green Hydrogen For Sustainable Industrial Development
Green Hydrogen represents a unique opportunity for the clean energy transition. Climate change is an existential threat to a sustainable future, but at the same time, facing up to the climate challenge is an opportunity to promote prosperity and a brighter future for all. Green hydrogen and its derivatives will play a vital role in the just energy transition.
Green Hydrogen For Sustainable Industrial Development
Green Hydrogen represents a unique opportunity for the clean energy transition. Climate change is an existential threat to a sustainable future, but at the same time, facing up to the climate challenge is an opportunity to promote prosperity and a brighter future for all. Green hydrogen and its derivatives will play a vital role in the just energy transition.
Bio-Ethanol: A More Sustainable Way to Produce Hydrogen
Hydrogen, often heralded as the fuel of the future, offers a beacon of hope for a sustainable energy transition. Its versatility and potential for clean energy production make it an invaluable asset in our collective quest for a carbon-neutral future. Hydrogen's role extends well beyond its potential in power generation and as a fuel, serving critical functions across several industrial sectors. The bulk of hydrogen production and consumption is dominated by refineries, chemical plants, and steel factories, which together account for around 90% of its usage. These sectors leverage hydrogen primarily for processing and manufacturing purposes, underscoring its importance in industrial applications rather than energy alone.
Bio-Ethanol: A More Sustainable Way to Produce Hydrogen
Hydrogen, often heralded as the fuel of the future, offers a beacon of hope for a sustainable energy transition. Its versatility and potential for clean energy production make it an invaluable asset in our collective quest for a carbon-neutral future. Hydrogen's role extends well beyond its potential in power generation and as a fuel, serving critical functions across several industrial sectors. The bulk of hydrogen production and consumption is dominated by refineries, chemical plants, and steel factories, which together account for around 90% of its usage. These sectors leverage hydrogen primarily for processing and manufacturing purposes, underscoring its importance in industrial applications rather than energy alone.