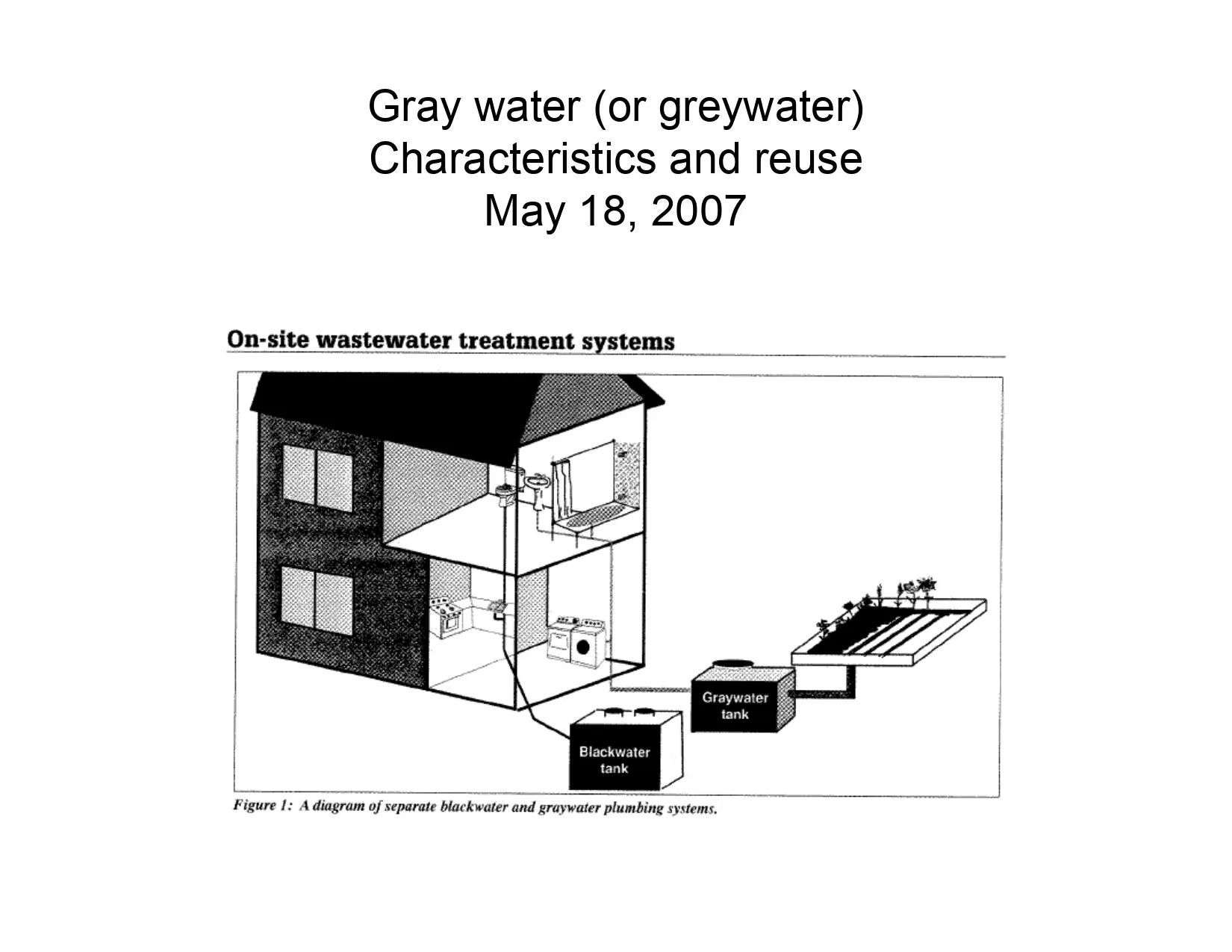
Onsite Water Reuse Systems In San Francisco, United States
Onsite Water Reuse Systems In San Francisco, United States
Greywater Use Guidelines For Residential Properties In Canberra
As cities expand and populations grow, the demand for water is rising. Factors, such as extended periods of drought combined with the social, economic and environmental costs of creating new water supplies, are leading us towards the need for better management of our water resources.
Greywater Use Guidelines For Residential Properties In Canberra
As cities expand and populations grow, the demand for water is rising. Factors, such as extended periods of drought combined with the social, economic and environmental costs of creating new water supplies, are leading us towards the need for better management of our water resources.
Guidelines For The Reuse Of Gray Water
With water reuse gaining popularity, people increasingly consider gray water from their residences as a resource to be separated from the wastewater stream and reused in their landscapes. Such reuse of gray water reduces the amount of wastewater entering sewers or individual wastewater systems (IWS), reduces demands to use potable water for other residential uses like irrigation, and helps preserve limited water supplies for essential uses like human consumption. These guidelines discuss using gray water resources simply and legally, at the same time protecting your family’s health, your neighborhood, and the environment.
Guidelines For The Reuse Of Gray Water
With water reuse gaining popularity, people increasingly consider gray water from their residences as a resource to be separated from the wastewater stream and reused in their landscapes. Such reuse of gray water reduces the amount of wastewater entering sewers or individual wastewater systems (IWS), reduces demands to use potable water for other residential uses like irrigation, and helps preserve limited water supplies for essential uses like human consumption. These guidelines discuss using gray water resources simply and legally, at the same time protecting your family’s health, your neighborhood, and the environment.