Water Desalination & RO
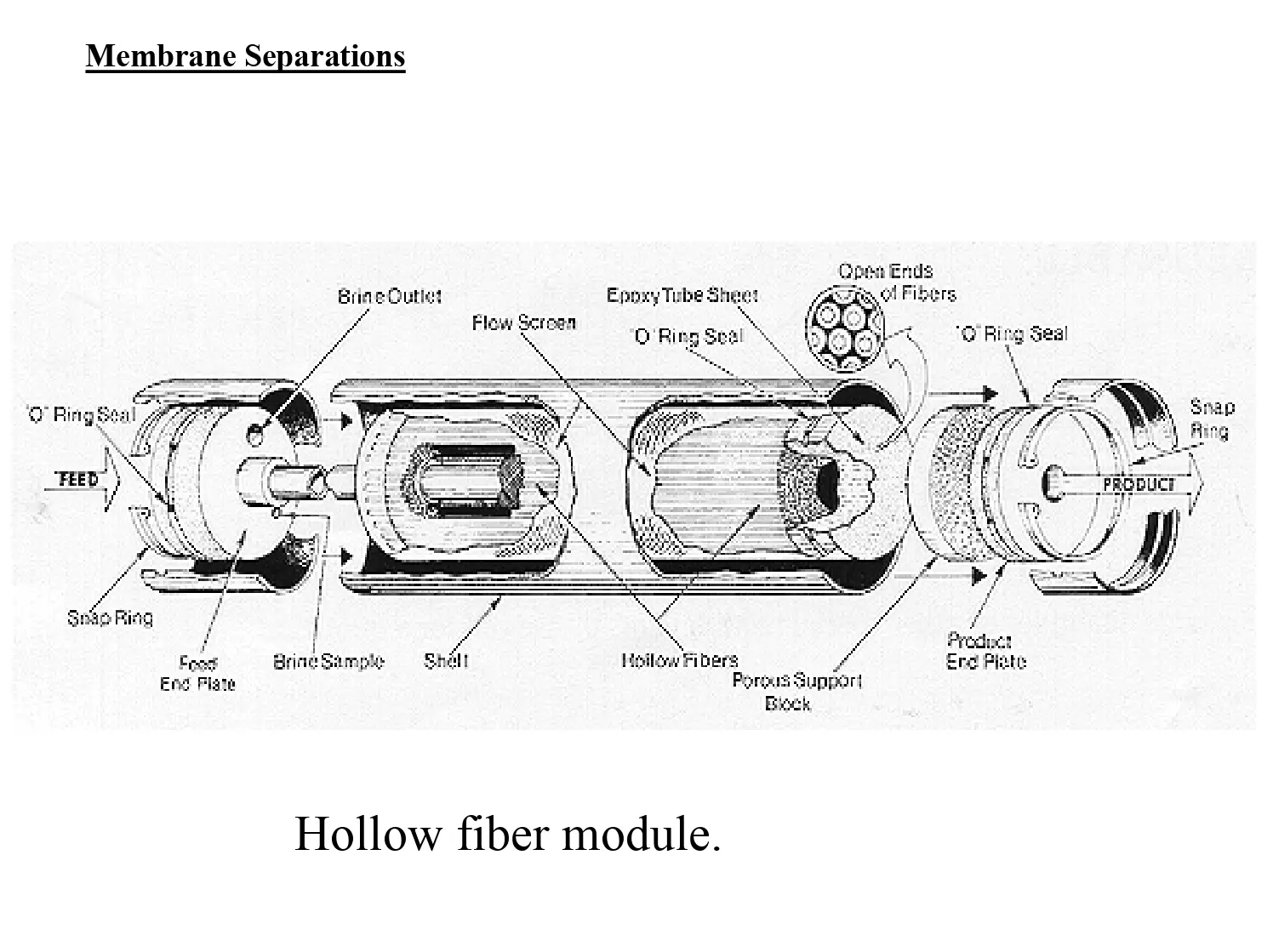
Membrane Separations: Hollow Fiber Module
Views : 8
Usually dispatched in 2 to 3 days
Usually dispatched in 2 to 3 days
Category:
Water Desalination & RO
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Related books
An Introduction To Membrane Techniques For Water Desalination
This course is adapted from the Unified Facilities Criteria of the United States government, which is in the
public domain, is authorized for unlimited distribution, and is not copyrighted.
An Introduction To Membrane Techniques For Water Desalination
This course is adapted from the Unified Facilities Criteria of the United States government, which is in the
public domain, is authorized for unlimited distribution, and is not copyrighted.
Desalination For Safe Water Supply
Preface:
Access to sufficient quantities of safe water for drinking and domestic uses and also for commercial and industrial applications is critical to health and well being, and the opportunity to achieve human and economic development. People in many areas of the world have historically suffered from inadequate access to safe water. Some must walk long distances just to obtain sufficient water to sustain life. As a result they have had to endure health consequences and have not had the opportunity to develop their resources and capabilities to achieve major improvements in their well being. With growth of world population the availability of the limited quantities of fresh water decreases. Desalination technologies were introduced about 50 years ago at and were able to expand access to water, but at high cost. Developments of new and improved technologies have now significantly broadened the opportunities to access major quantities of safe water in many parts of the world. Costs are still significant but there has been a reducing cost trend, and the option is much more widely available. When the alternative is no water or inadequate water greater cost may be endurable in many circumstances.
Desalination For Safe Water Supply
Preface:
Access to sufficient quantities of safe water for drinking and domestic uses and also for commercial and industrial applications is critical to health and well being, and the opportunity to achieve human and economic development. People in many areas of the world have historically suffered from inadequate access to safe water. Some must walk long distances just to obtain sufficient water to sustain life. As a result they have had to endure health consequences and have not had the opportunity to develop their resources and capabilities to achieve major improvements in their well being. With growth of world population the availability of the limited quantities of fresh water decreases. Desalination technologies were introduced about 50 years ago at and were able to expand access to water, but at high cost. Developments of new and improved technologies have now significantly broadened the opportunities to access major quantities of safe water in many parts of the world. Costs are still significant but there has been a reducing cost trend, and the option is much more widely available. When the alternative is no water or inadequate water greater cost may be endurable in many circumstances.
Assessment Of Best Available Technologies For Desalination In Rural/Local Areas
Introduction: The Sustainable Water Integrated Management (SWIM) is a European Union(EU)-funded Regional Technical
Assistance Program [1] that “aims at supporting water governance and mainstreaming by promoting sustainable
and equitable water resources management to become a prominent feature of national development policies and
strategies (agriculture, industry, tourism, etc).” [2]
Countries in the south of the Mediterranean are facing increasing water scarcity. This scarcity is driving the need
for augmenting conventional water supply with alternative water sources. Rural and remote areas are particularly
disadvantaged because such areas are often located far away from municipal water supply systems and
conventional water sources, and are often not connected to the electric power grid. There is good potential for
addressing the water scarcity problem in rural and remote areas through sustainable saline water desalination
technologies. Seawater and brackish water desalination are well-established industries comprising a wide variety
of available technologies with decades of accumulated experience. There are many advancements and evolution in
desalination technologies. The numerous technologies and processes available have different characteristics,
advantages and disadvantages that make each suitable for particular market segments or specific niches.
Moreover, much of the cumulative technology experience is related to large urban supply plants that are either
connected to the grid, or are themselves part of large power and desalination cogeneration plants. Rural and
remote areas have special requirements that influence the appropriate selection of technologies. These include
technical requirements related to small-scale application using renewable energy sources, ease of operation and
maintenance, and simple design; requirements dictated by geographical location; as well as socio-economic and
socio-cultural requirements related to the communities that are intended to operate and benefit from the
technology. Successful implementation and long term sustainability (operational and environmental sustainability)
of desalination projects for rural and remote locations requires that all the relevant requirements be identified and
addressed from the earliest stages of the project.
Assessment Of Best Available Technologies For Desalination In Rural/Local Areas
Introduction: The Sustainable Water Integrated Management (SWIM) is a European Union(EU)-funded Regional Technical
Assistance Program [1] that “aims at supporting water governance and mainstreaming by promoting sustainable
and equitable water resources management to become a prominent feature of national development policies and
strategies (agriculture, industry, tourism, etc).” [2]
Countries in the south of the Mediterranean are facing increasing water scarcity. This scarcity is driving the need
for augmenting conventional water supply with alternative water sources. Rural and remote areas are particularly
disadvantaged because such areas are often located far away from municipal water supply systems and
conventional water sources, and are often not connected to the electric power grid. There is good potential for
addressing the water scarcity problem in rural and remote areas through sustainable saline water desalination
technologies. Seawater and brackish water desalination are well-established industries comprising a wide variety
of available technologies with decades of accumulated experience. There are many advancements and evolution in
desalination technologies. The numerous technologies and processes available have different characteristics,
advantages and disadvantages that make each suitable for particular market segments or specific niches.
Moreover, much of the cumulative technology experience is related to large urban supply plants that are either
connected to the grid, or are themselves part of large power and desalination cogeneration plants. Rural and
remote areas have special requirements that influence the appropriate selection of technologies. These include
technical requirements related to small-scale application using renewable energy sources, ease of operation and
maintenance, and simple design; requirements dictated by geographical location; as well as socio-economic and
socio-cultural requirements related to the communities that are intended to operate and benefit from the
technology. Successful implementation and long term sustainability (operational and environmental sustainability)
of desalination projects for rural and remote locations requires that all the relevant requirements be identified and
addressed from the earliest stages of the project.
Desalination Needs and Appropriate technology
Abstract
This study investigates the desalination needs and available technologies in Sri Lanka. Lack of rainfall, pollution due to agricultural chemicals, presence of fluoride, increasing demand, exploitation of ground water and brackishness have created scarcity of fresh pure water specially in near costal and dry zones in Sri Lanka. Due to Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) around 500 people died in dry zones annually which is suspected to cause by Arsenic and Cadmium contain
in ground water due to agriculture chemicals. The available desalination methods are Reverse Osmosis (RO), Solar distillation and conventional methods. The cost for RO is Rs.0.10 cents per liter and solar distillation Rs.2.96 per liter. Although the price shows that the RO is better but due to high initial investment as a
third world country it is very difficult to afford huge initial investment without government intervention. The experimental solar desalination units only produce nearly 5liters of potable water per day and directly impacted by availability of solar radiation.
The energy availability of Sri Lanka and future potable water demand predicted as 2188.3 Mn liters as maximum demand which will be in 2030, therefore by that time the government should have a proper plan to cater the demand and desalination plants need to be planned and built based on the demand of dry zones and specially agriculture areas. The applicability of renewable energy for desalination in local arena was also simulated taking the Delft Reverse Osmosis plant for the simulation. Results show that the optimum design is combination of Solar PV and existing 100kW Diesel generator Set with Battery bank and
converter.
Desalination Needs and Appropriate technology
Abstract
This study investigates the desalination needs and available technologies in Sri Lanka. Lack of rainfall, pollution due to agricultural chemicals, presence of fluoride, increasing demand, exploitation of ground water and brackishness have created scarcity of fresh pure water specially in near costal and dry zones in Sri Lanka. Due to Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) around 500 people died in dry zones annually which is suspected to cause by Arsenic and Cadmium contain
in ground water due to agriculture chemicals. The available desalination methods are Reverse Osmosis (RO), Solar distillation and conventional methods. The cost for RO is Rs.0.10 cents per liter and solar distillation Rs.2.96 per liter. Although the price shows that the RO is better but due to high initial investment as a
third world country it is very difficult to afford huge initial investment without government intervention. The experimental solar desalination units only produce nearly 5liters of potable water per day and directly impacted by availability of solar radiation.
The energy availability of Sri Lanka and future potable water demand predicted as 2188.3 Mn liters as maximum demand which will be in 2030, therefore by that time the government should have a proper plan to cater the demand and desalination plants need to be planned and built based on the demand of dry zones and specially agriculture areas. The applicability of renewable energy for desalination in local arena was also simulated taking the Delft Reverse Osmosis plant for the simulation. Results show that the optimum design is combination of Solar PV and existing 100kW Diesel generator Set with Battery bank and
converter.
Tailoring Advanced Desalination Technologies for 21st Century Agriculture
Abstract: Substantial parts of the U.S., particularly drier landlocked regions, are facing acute water shortages and water quality issues that decrease agricultural productivity. Reduced crop yields cause billions of dollars in losses annually, affecting the livelihoods of thousands. A combination of population growth, inefficient agricultural practices, and resource demanding consumption trends is only expected to increase pressure on our water supplies. This research proposal seeks to address water and food security issues by cost-effectively and energy-efficiently enhancing water quality and water supply in greenhouses; a $22.93 billion dollar industry in 2017 that is rapidly growing at an annual rate of 8.92%. Greenhouses widely practice desalination of salty irrigation water to improve their operations. However, currently used desalination methods do not tailor greenhouse waters based on crop requirements. This work investigates a fully integrated desalination solution that treats and tailors brackish source waters ingreenhouses to save fertilizer and water. Specifically, this project experimentally studies multi-ion transport in and assesses the economic viable of monovalent selective electrodialysis (MSED). MSED allows for the selective removal of monovalent ions damaging to crops and the retention of divalent ions beneficial for crops, unlike the widely used reverse osmosis (RO), which removes all ions from greenhouse source water. First, we evaluate the techno-economic feasibility of MSED compared to other brackish desalination technologies for agricultural applications, based on primary market research we conduct with over 70 greenhouses.
These include conventional technologies, such as reverse osmosis (RO) and electrodialysis (ED), and advanced technologies, such as closed circuit reverse osmosis (CCRO). The analysis determines the levelized costs of water, the capital costs and energy requirements of these technologies, and how these vary with feed salinity, system capacity and recovery ratio. Then, we build a bench-scale setup to experientially characterize MSED membrane properties, including monovalent selectivity, ion transport, limiting current and resistance, for multiple brackish feedwaters and for two sets of MSED membranes: the widely used Neosepta ACS/CMS membranes and the new Fujifilm Type 16 membranes. Both MSED membranes show notable monovalent selectivity for all tested compositions, reflecting the potential of the technology for selective desalination in greenhouses. The measurements are compared to a model for MSED in multi-ion solutions. The model predicts multi-ion transport for the Neosepta and Fujifilm MSED systems within 6% and 8%, respectively.
Tailoring Advanced Desalination Technologies for 21st Century Agriculture
Abstract: Substantial parts of the U.S., particularly drier landlocked regions, are facing acute water shortages and water quality issues that decrease agricultural productivity. Reduced crop yields cause billions of dollars in losses annually, affecting the livelihoods of thousands. A combination of population growth, inefficient agricultural practices, and resource demanding consumption trends is only expected to increase pressure on our water supplies. This research proposal seeks to address water and food security issues by cost-effectively and energy-efficiently enhancing water quality and water supply in greenhouses; a $22.93 billion dollar industry in 2017 that is rapidly growing at an annual rate of 8.92%. Greenhouses widely practice desalination of salty irrigation water to improve their operations. However, currently used desalination methods do not tailor greenhouse waters based on crop requirements. This work investigates a fully integrated desalination solution that treats and tailors brackish source waters ingreenhouses to save fertilizer and water. Specifically, this project experimentally studies multi-ion transport in and assesses the economic viable of monovalent selective electrodialysis (MSED). MSED allows for the selective removal of monovalent ions damaging to crops and the retention of divalent ions beneficial for crops, unlike the widely used reverse osmosis (RO), which removes all ions from greenhouse source water. First, we evaluate the techno-economic feasibility of MSED compared to other brackish desalination technologies for agricultural applications, based on primary market research we conduct with over 70 greenhouses.
These include conventional technologies, such as reverse osmosis (RO) and electrodialysis (ED), and advanced technologies, such as closed circuit reverse osmosis (CCRO). The analysis determines the levelized costs of water, the capital costs and energy requirements of these technologies, and how these vary with feed salinity, system capacity and recovery ratio. Then, we build a bench-scale setup to experientially characterize MSED membrane properties, including monovalent selectivity, ion transport, limiting current and resistance, for multiple brackish feedwaters and for two sets of MSED membranes: the widely used Neosepta ACS/CMS membranes and the new Fujifilm Type 16 membranes. Both MSED membranes show notable monovalent selectivity for all tested compositions, reflecting the potential of the technology for selective desalination in greenhouses. The measurements are compared to a model for MSED in multi-ion solutions. The model predicts multi-ion transport for the Neosepta and Fujifilm MSED systems within 6% and 8%, respectively.
Desalination: A National Perspective
NOTICE:
The project that is the subject of this report was approved by the Governing Board of the National Research Council, whose members are drawn from the councils of the National Academy of Sciences, the National Academy of Engineering, and the Institute of Medicine. The members of the panel responsible for the report were chosen for their special competences and with regard for appropriate balance.
Support for this study was provided by the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation under Grant No. 06CS811198. Any opinions, findings, conclusions, or recommendations expressed in this publication are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the organizations or agencies that provided
support for the project.
Desalination: A National Perspective
NOTICE:
The project that is the subject of this report was approved by the Governing Board of the National Research Council, whose members are drawn from the councils of the National Academy of Sciences, the National Academy of Engineering, and the Institute of Medicine. The members of the panel responsible for the report were chosen for their special competences and with regard for appropriate balance.
Support for this study was provided by the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation under Grant No. 06CS811198. Any opinions, findings, conclusions, or recommendations expressed in this publication are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the organizations or agencies that provided
support for the project.
Desalination and Membrane Technologies: Federal Research and Adoption Issues
In the United States, desalination and membrane technologies are used to augment municipal water supply, produce high-quality industrial water supplies, and reclaim contaminated supplies (including from oil and gas development). Approximately 2,000 desalination facilities larger than
0.3 million gallons per day (MGD) operate in the United States; this represents more than 2% of U.S. municipal and industrial freshwater use. At issue for Congress is what should be the federal role in supporting desalination and membrane technology research and facilities. Desalination issues before the 114th Congress may include how to focus federal research, at what level to support desalination research and projects, and how to provide a regulatory context that protects the environment and public health without disadvantaging desalination’s adoption.
Desalination and Membrane Technologies: Federal Research and Adoption Issues
In the United States, desalination and membrane technologies are used to augment municipal water supply, produce high-quality industrial water supplies, and reclaim contaminated supplies (including from oil and gas development). Approximately 2,000 desalination facilities larger than
0.3 million gallons per day (MGD) operate in the United States; this represents more than 2% of U.S. municipal and industrial freshwater use. At issue for Congress is what should be the federal role in supporting desalination and membrane technology research and facilities. Desalination issues before the 114th Congress may include how to focus federal research, at what level to support desalination research and projects, and how to provide a regulatory context that protects the environment and public health without disadvantaging desalination’s adoption.














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.